Introduction to Jigs and fixtures
Introduction
Interchangeability to facilitate easy assembly along with cost savings are the most important factors in the successful implementation of a mass production. Easy and fast positioning work is important for precise operation on Mass production methods.
Two key manufacturing tools that help make precisely reproducible and interchangeable parts precisely are the Jigs and the fixtures. The jigs and fixtures are specially designed that can machine or assemble large numbers of components and easily assure the manufacturer that they can be easily replaced or interchanged any of components.
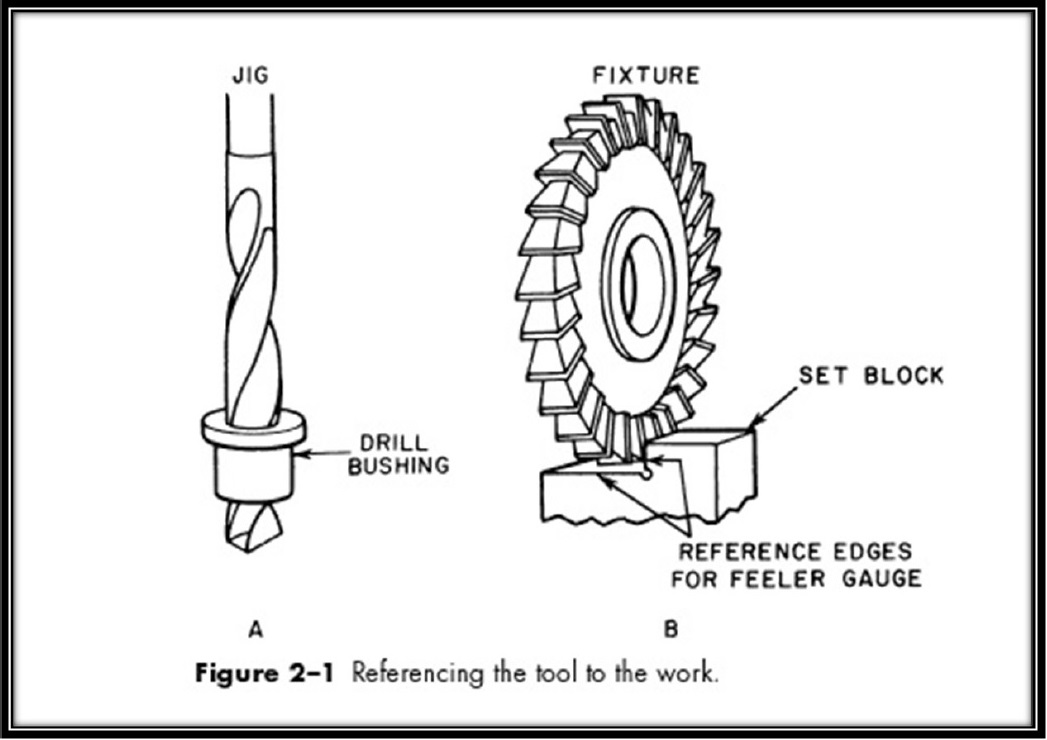
JIGS
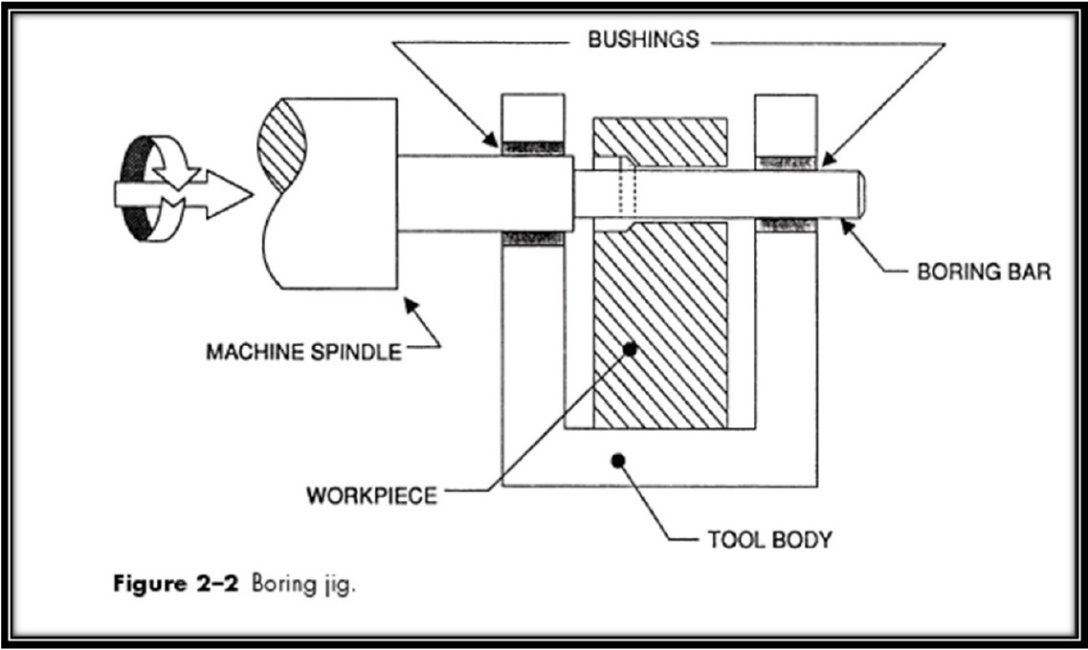
Jigs are tools that help the machine hold and work as a maintainer, support and fix the components, and guide the cutter through various operations. Jigs are made of hard metal bushes and are a type of tool that both help control the location and help guide and move another tool.
In fact, the main reason for the production and use of a tool called a jig in machine tools is to create repeatability, and to increase the accuracy and speed of replacement of parts to produce different products. Jigs do both job-keeping and tool-handling.
When a key is duplicated, we have an example of a jig that is originally used as a jig and the newly created key can be used in any other path that may be similar to the previous one.
FIXTURES
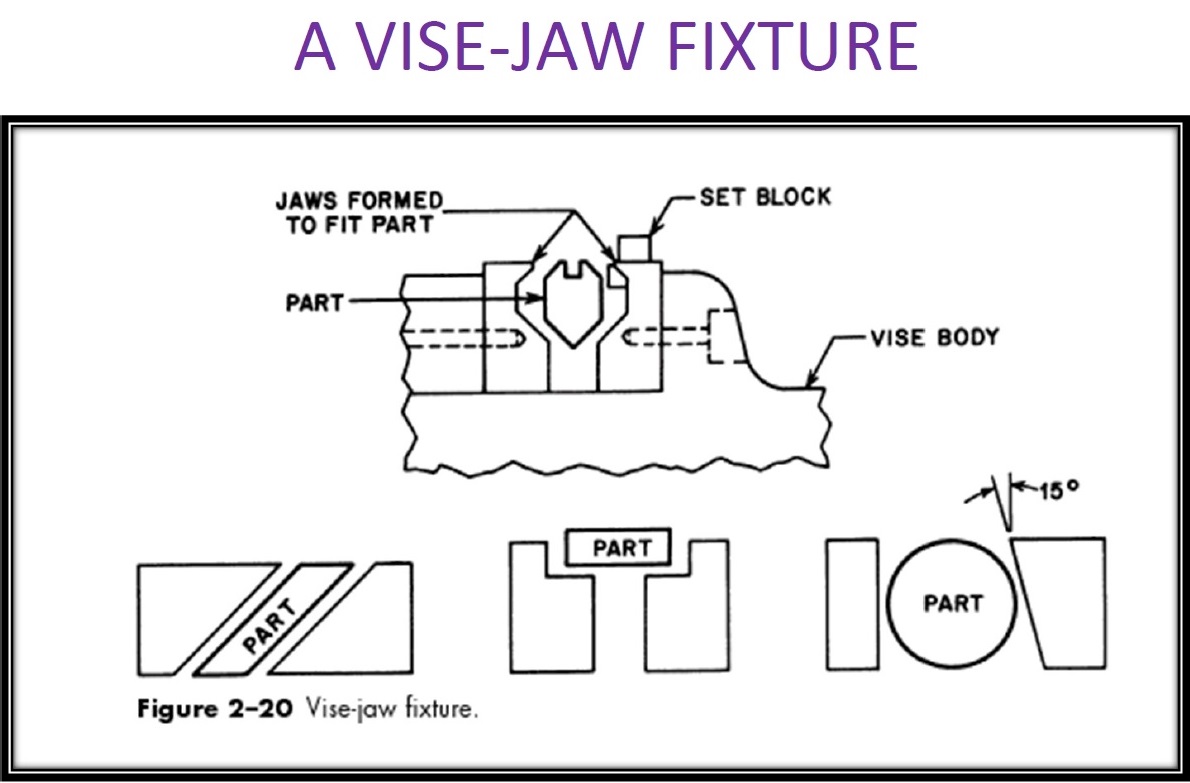
The fixture, as its name implies, is a tool that holds and supports a set of work to perform a series or a particular task, but unlike the jigs, does not guide the cutting tool. The fixture actually provides the user with a reference work surface or a device. Given that the fixtures are each designed to fit a particular part or shape, it can be said that the fixtures are very unique.
In essence, the main purpose of installing and using fixtures on a device for a series of specific operations or some industrial process is to maintain a workpiece. This differentiates jigs with fixtures, because jigs in addition to fixing and holding the workpiece also guide the working tool to the correct position.
Such as Vises, chucks
What are the most important differences between jigs and fixtures?
| jigs | fixtures |
| 1. It is a type of work holding device that can support and direct the workpiece while guides a precision cutting tool for specific activities. | 1. It is a workpiece holder device that only supports and holds the workpiece but is not designed for cutting tool guides. |
| 2. To work with jigs, you do not need to attach them to the drill press unless you need to make large holes on the workpiece, in which case you have to move the jig straight for each bush directly under the drill. | 2. To work with the fixture, it must be securely fastened to the machine table to be used..
|
| 3. To perform special operations such as drilling, reaming, tapping and other boring tasks usually used of jigs that are special tools. | 3. Unlike Jigs, fixtures are special tools commonly used in milling machines, shaping machines or slot machines. |
| 4. In Jigs, block gauges are not commonly used. | 4. In fixtures, a block gauge is best used for effective control. |
| 5. The construction of jigs is lighter than fixtures | 5. The construction of fixtures are heavier than jigs |
Advantages of Jigs and Fixtures
PRODUCTIVITY:
Jiggs and fixtures are very effective devices for increasing productivity because they eliminate individual marking and cause frequent positioning and checking. As well as speeding up work, feed and depth cutting due to their very high grip strength, they save a lot of time on the job.
INTERCHANGEABILITY AND QUALITY:
Production of high quality and ultra-high precision, uniform quality and interchangeable, and sure at a significant competitive cost, are a features of Jigs and fixtures that simplify and accelerate the process.
- SKILL REDUCTION:
You do not need to have special skills to set up the tool. One of the biggest benefits of the Jigs and fixtures is that even ordinary and unskilled or semi-skilled machine operator can work with them, which can save a lot of money.
- COST REDUCTION:
Using Jiggs and fixtures the final cost of the unit will be greatly reduced as not only will the production rate increase but also the amount of waste reduced and assembly easier.
Fundamental principles of Jigs and Fixtures design
LOCATING POINTS:
To locating a work you have to have the best facilities. Parts that need machining must be such that they are easily fitted into the Jigs machine and come out easily so that it does not take too long to assemble the workpiece. The position of the workpiece must be carefully adjusted according to the tool guiding in the jig or the fixing of elements in the fixture.
FOOL PROOF:
The type of design of the jigs and fixtures should be such as not to allow the workpiece to be misaligned elsewhere in the machine and to ensure that the workpiece is precisely adjusted.
- IDLE TIME REDUCTION:
To minimize the work time, the Jigs or fixtures should be designed to allow the process of loading, clamping and unloading the workpiece quickly and without time outages.
- JIGS AND FIXTURES WEIGHT:
Without sacrificing the rigidity and stiffen, based on the material, the size of the Jigs and fixtures should be considered as small as possible to reduce costs and facilitate control and management.
- JIGS PROVIDED WITH FEET:
Sometimes the Jigs are designed and built with feet, to fit the Jigs on the device table.
- MATERIALS FOR JIGS AND FIXTURES:
Jigs and fixtures should be made of materials that are highly resistant to abrasion to withstand frequent wear and tear, such as: MS, Cast iron, Diesteel, CS, HSS.
CLAMPING DEVICE:
These machines CLAMPING should be as simple as possible without affecting the effectiveness of the work. Jigs clamps or fixtures must be extremely strong to hold the workpiece extremely tight while also controlling the strain of the cutting tool when working on the workpiece.
Essential features of Jigs and Fixtures
- Reduction of idle time –
The clamping and unloading time of the workpiece must be such as to provide the machine with a minimum shutdown time
- Cleanliness of machining process –
The design of the device should not be handled in such a way as to waste a lot of time on cleaning the scarfs, chips, cuttings, burrs etc.
- Replaceable part or standardization –
The locating and supporting surfaces should be standardized to the extent that they are interchangeable so that they can be easily constructed interchangeably.
- Provision for coolant –
An adequate Provision should be provided for cooling the tools and for washing the strings and chips.
- Hardened surfaces
As far as conditions allow, hardened and water-soluble materials should be used to build all of the Jigs and fixtures locating and supporting surfaces, in order to avoid immediate wear and tear and loss of precision in less time.
- Inserts and pads
In order not spoilt, it is always advisable to attach parts of the clamps that are in contact with the finished surfaces of the workpiece.
- Fool-proofing
Pins and other devices of simple nature incorporated in such a position that they will always spoil the placement of the component or hinder the fitting of the cutting tool until the latter are in correct pos
Simple nature incorporated such as pins and some other devices are usually always in situations that can spoil the placement of the component or prevent the cutting tool from being installed simply until the latter are in correct pos .
- Economic soundness
The cost of designing and manufacturing equipment must be commensurate with the quantity and price of the manufacturer in order to be economically sound
- Easy manipulation
Manufacturing of these equipment should be used with the utmost care to create light weight and at the same time be easy to operate so as not to overwhelm the operators and workers and should have sufficient lifting aids.
- Initial location
To ensure proper Initial location, it must be ensured that the workpiece is not positioned at more than 3 points on each test plane to ensure that no rocking is present and that there should be spring loading.
- Position of clamps
To prevent distortion and springing, the Clamping should be done directly above the workpiece support points.
- Clearance
Sufficient working Clearance must be seen around the device so that the operator can work comfortably with his hands easily inserted into the body of the device to position the workpiece without any distortions or errors in loading the workpiece and threaten the worker’s safety. Don’t.
- Ejecting devices
In order for the workpiece to be ejected easily after the operation, appropriate ejecting devices must be fitted to pull the workpiece into the body of the device.
- Rigidity and stability
Equipment must maintain good stability and rigidity when operating. In principle, the predictions be made for good position and rigidly holding the Jigs and fixtures
- Safety
The design must ensure the maximum safety of the device operator.
General rules for designing jigs and fixtures
- The cost of making the machines should not exceed the expected profit, so it is best to compare the cost of producing the work with the available tools and the expected cost of manufacturing with the cost of the tool being built to estimate the cost in advance.
- Before making the devices, it is best to decide on the location and order of the outline clamping.
You should consider all devices and their connections as quickly as possible. - Get approval and fool proof for Jiggs
- Some location points should always be considered adjustable.
- Try not to make any complicated clamping arrangements
- You have to round out all the corners.
- Wherever possible, Provide handles
- Allow plenty of work clearance
- You must consider holes to drain the chips.
- Care must be taken when adjusting the clamps to provide maximum resistance when working.
- All clamps should be as far as possible Placed opposite some bearing point of the work as far as possible to avoid spring action.
- Before using the machine in the shop, it is best to do all the testing required by Jigs as soon as possible.
MATERIALS USED
There are various types of Jigs and fixtures, each made for a variety of purposes, some of which are much more resistant to wear and tear.
Frequently used materials for the manufacture of Jigs and Fixtures:
High Speed Steel:
For making cutting tools such as milling cutters, reamers or drills
Die steels:
For the manufacture of parts such as presses, it contains 1% carbon, 0.5% to 1% tungsten, and slightly silicon and manganese.
Carbon steel:
It is often used to produce standard cutting tools
Collet steel:
For the production of spring steel, it contains 1% carbon, 0.5% manganese and very little silicon.
Non shrinking tool steels
High carbon or chromium content to minimize wear and tear during high heat treatment. This type of steel is often used for the production of large and sophisticated press tools.
Nickel chrome steel:
It is often used to produce parts such as gears.
High tensile steel
It is often used for connectors such as high tensile screws.
Mild steel
This type of steel is used in most parts of the Jigs and fixtures and is the cheapest type of steel to produce these machines, which has about 0.03% carbon.
Cast iron
This type of metal is often used for the production of exotic shaped parts in some laborious machines.
This type of metal has a CI for casting patterns
More than 2 percent contains carbon
Particularly good lubrication
It has high resistance to vibration and is a great option for base mounting.
Nylon and Fiber:
This material is used as a soft lining to clamps parts exposed to workpiece damage due to clamping pressure.
Phosphorus bronze:
Used in nuts and because of its high tensile strength and ruggedness, it is an excellent choice for lead screw nuts.
Some of the most important factors to consider when designing jigs and fixtures:
- Compounds
Jigs and fixtures should be designed to cover the maximum operation required for the work process and minimize interruption. For this purpose, all factors must be carefully examined to ensure that the work is done in a proper sequence.
- Device capacity
Depending on the type of operation expected, the capacity and type of device must be carefully considered.
- Production requirements
The design of the apparatus should be based on the actual production needs and also the manual and automatic tool arrangements which should be considered after the actual production needs.
- Location
- On location, the distribution of forces should be well thought out throughout the sequence of the operation
- Location must have met criteria such as hardness, abrasion resistance and high accuracy.
- There should be the least movement of the workpiece
- fool proofed must be considered to make sure the workpiece is not in the wrong place.
- The workload should be as simple and fast as possible.
- Unnecessary locators should not be used.
- All corners should be rounded and there should be no sharp corners in the location
- A minimum datum level must be established
- Workpiece loading and unloading arrangements
- Sufficient space or adequate clearance must be provided for loading and unloading of the workpiece from device
- This space should be large enough to allow for speed and ease of operation.
- Variation of the size must be well considered and accepted
- The workpiece must be of the hard and dry type of material and should not be sticky.
- Clamping arrangements or settings
- High-speed action clamps should be used as far as possible
- the clamps should not be selected in such a way as to alter the shape of the workpiece and cause any deformation on workpiece
- clamps should always be mounted on top of the support work points
- Power-driven clamps are high-speed, comfortable, controllable, and reliable clamps that can be used for operation without altering or causing any fatigue to the workpiece.
- Key features of the clamp:
- It should provide the least pressure at closing time.
- There should be no distortions on the workpiece when used
- It must be simple and fool proof
- It should have the least amount of movement
- In order to prevent wear, it must be made of a hard and suitable material
- It should be strong enough to prevent the piece from bending
- Required Clearance between jig and combinations
- The Clearance required should be designed in such a way as to allow different sizes of work on the workpiece
- The space should be large enough for the chips to pass easily
- Ejectors-
- Ejectors must be incorporated to remove the work from clamping locators
- These ejectors should be such that they discharge a piece of equipment with high speed and accuracy and thereby increase the rate of production.
- Design and construction of machine base and body
- The design and construction of the base and body must include machining, casting, welding, fabrication, forging and machining.
- Tool guiding and cutting adjustment
- Using a cutting adjustment block, the machine has to adjust the cutting adjustment task for the cut relative to working on a fixture. To do this, drill bushes embedded on the jig plates should be carefully designed and carefully machined.
- Strength and vibration of the device
- Devices should be designed to withstand the least vibration with the strongest.
- Shaking the device can cause unwanted movements of the workpiece and tool, and may even pose risks to operators and may reduce precision.
- Safety
- The device must be designed to provide the highest safety coefficient for operation with the device.
- Cost
- In order to reduce costs, even a simple device should be designed and manufactured.
- The costs incurred should be optimized as much as possible.
- Generally used substances
- It is best to consider the following materials for the manufacture of each device:

